Description
![]()
Welcome to optical quantitative telescope alignment !
SkyWave Collimator unlimited (UNL) mathematical models (450S) for reflector telescopes with apertures (diameters) greater than (>) to 330mm, or 13″.
Model for SkyWave (SKW) and for SkyGuide and SkyGuard (SKG) versions supporting SKW.
Key and useful documentation and information links to visit:
Full SkyGuide, SkyGuard and SkyWave-Collimator version interactive help and documentation
SkyWave collimator tool proper setup for telescope alignment (PDF)
SkyWave: Dealing with seeing (PDF)
Alignment of Cassegrain type of telescopes having at least one spherical mirror (such as SCT, CDK, iDK) with SKW (PDF)
Alignment of Ritchey–Chrétien Telescopes (RCT) with SKW (PDF)
Please read all the information below before purchasing your model.
This is an unlimited (UNL) model to be used for analyzing with SKW an unlimited amount of images.
This model is limited to reflector telescopes with an aperture (diameter) greater than (>) to 330mm, or 13″.
For larger apertures and pay per use (PPU) models please browse our on-line store for compatible models.
This is an order only, to be used for requesting an actual model within SKW (instrument panel, see documentation), there is no download.
The encrypted model file will be sent electronically to the customer after Innovations Foresight has received a model request using SKW by the user. This SKW request must include the order confirmation number issued after purchasing this model, see the field “IF! Order #”.
Below an example of a permanent model request with the confirmation number # 12345:
After the request of a model within SKW, depending of the telescope specifications, it may take some days for its generation before it can be send electronically to the customer.
Please review carefully the model 420S specifications, data and plots, below since once a model has been sent to the user, after his request in SKW, it can not be refunded.
Pay specifically attention at the required defocus value in microns, intra or extra focal.
The customer is responsible to achieve such defocus either by using an external focuser and/or the scope mirror focusing system, if any. In the latter case the SKW reported spherical aberrations may not be accurate anymore, coma and astigmatism are still accurate as long as the SKW measured defocus travel value is within the tolerance range for a given telescope optics, see specifications.
When requesting a model in SKW the user needs to select either an intra (before the focal plane) or extra (after the focal plane) focal model.
We recommend selecting extra focal whenever possible, however due to mechanical motion restriction and/or interference of the focusing mechanism an intra-focal model may be required. A model is only issued for one defocus direction (intra or extra), the customer is responsible for selecting the correct defocus direction during the request process in SKW/SKG.
Changing the defocus direction on the SKW Collimator version requires buying a new model, see our on line-store for model defocus direction conversion (extra <-> intra).
The model remains valid if the user changes, in SKW, the wavelength, the seeing or specifies a reduction/expansion factor in the related instrument setting to account for a focal reducer or a extender, within this option tolerance.
Specifications:
| Recommended wavefront range | Max=700nm | Min=300nm | We recommend using a red filter (~650nm) for seeing reduction |
| Central obstruction relative to scope aperture (diameter) |
Max=50% | Min=30% | For other values please contact us. For a refractor please select a refractor model in the store |
| Aperture (diameter) |
Max=1000mm | Min>330mm (13″) |
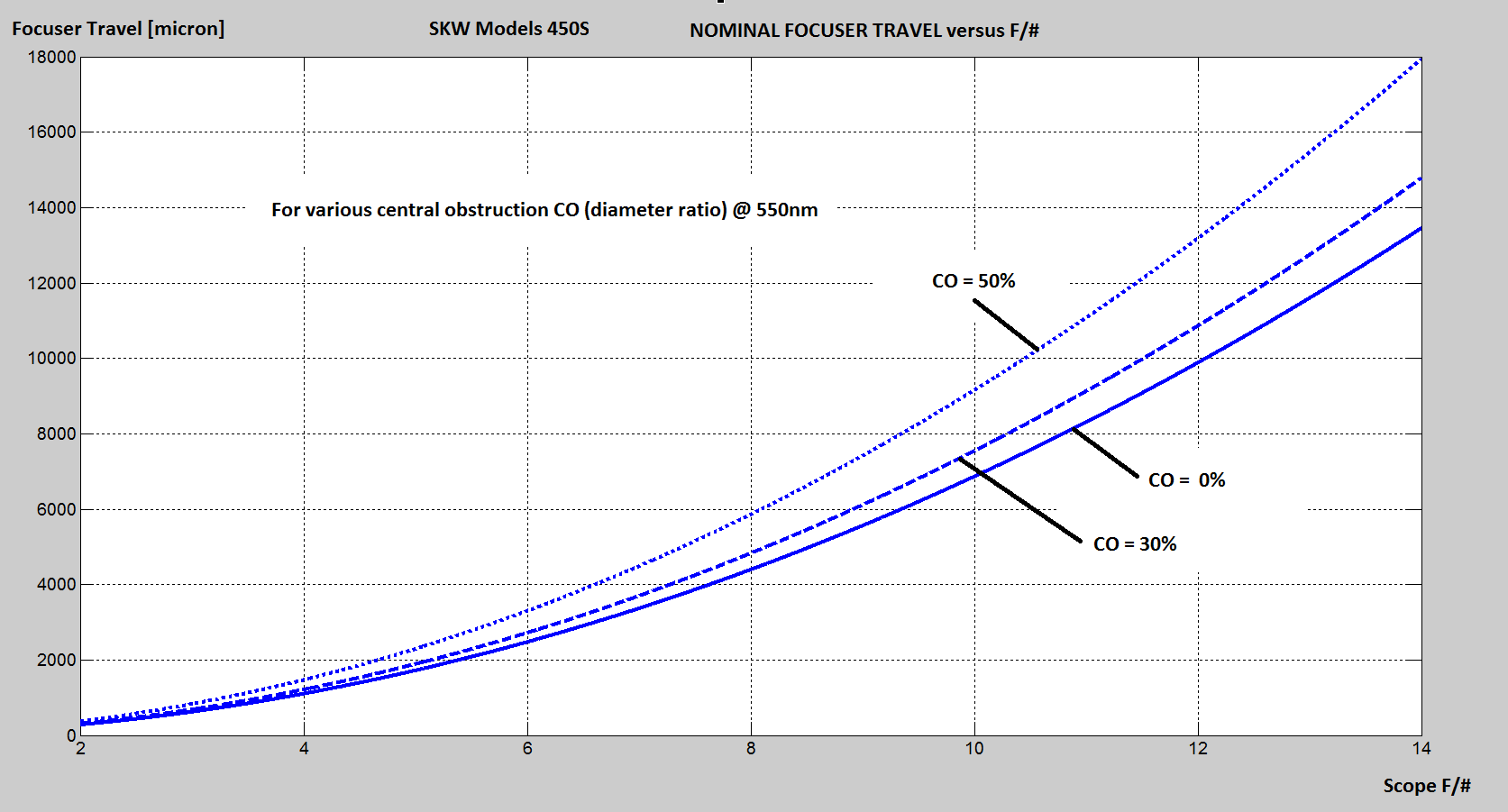
Nominal defocus travel required intra or extra focal @ 550nm, see plot below:
Caution: The travel value is a function of the scope F/# and CO values, as well as the wavelength used during the SKW analysis.
To compute a new focuser travel distance (NewFocuserTraverl@Lambda) when using a wavelength (Lambda), in nm, different than the @ 550nm employed in the plot below (FocuserTravel@550nm), use the following formula:
NewFocuserTraverl@Lambda = FocuserTravel@550nm X Lambda / 550
Example: Scope f/# = 8, CO = 50%, from the plot below, @ 550nm, FocuserTravel@550nm = 6000 microns.
If lambda = 640nm the NewFocuserTravel@lambda = 6000 X 640 / 550 = 6982 microns, almost one full millimeter longer.
The customer is responsible to achieve such defocus either by using an external focuser and/or the scope mirror focusing system, if any. In the latter case the SKW reported spherical aberrations may not be accurate anymore, coma and astigmatism are still accurate as long as the SKW measured defocus travel value is within the tolerance range for a given telescope optics. Whenever possible we recommend to use the extra focal model.
Recommended imaging camera pixel size @550nm, see plot below:
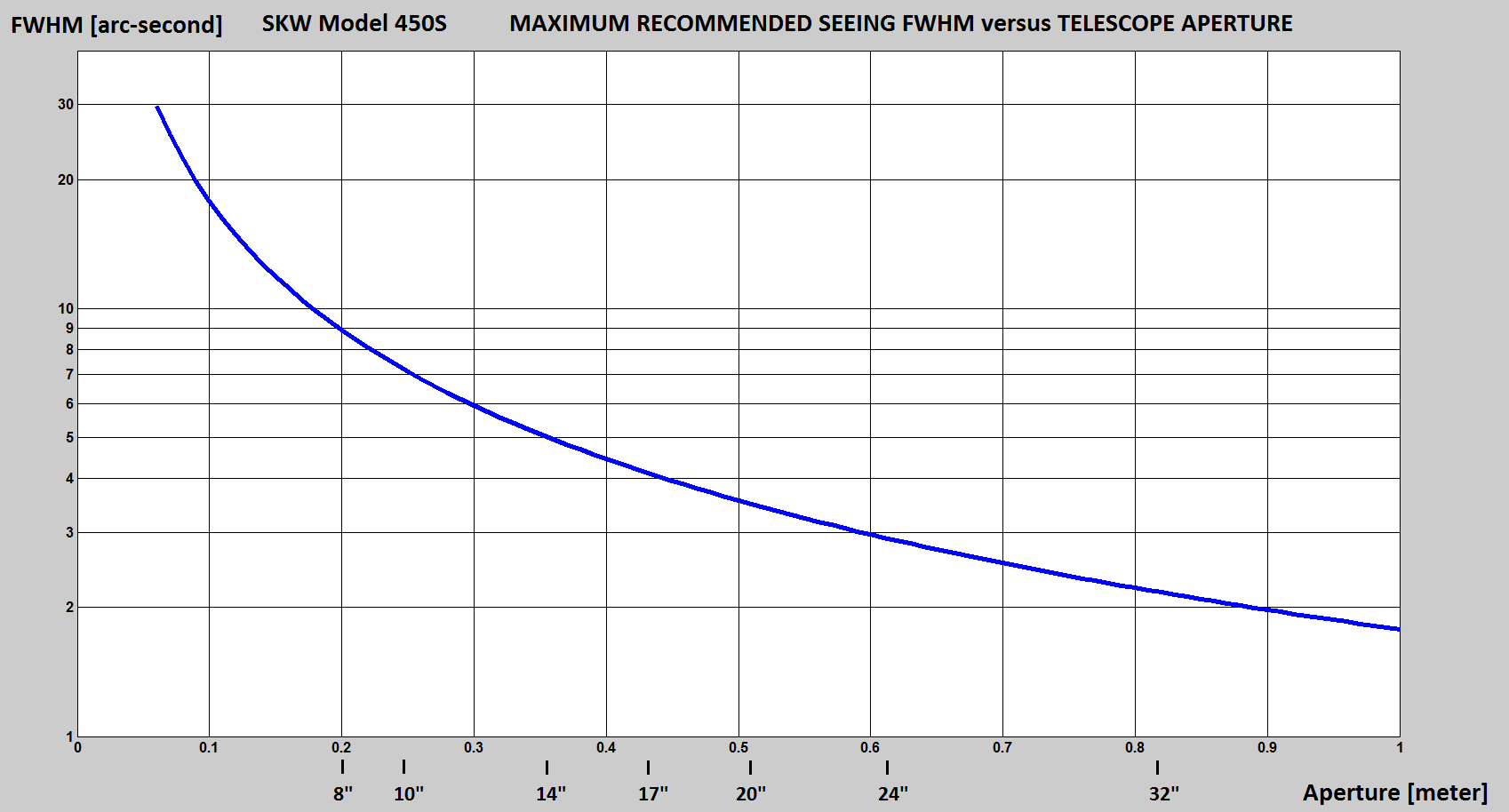
Maximum recommended seeing FWHM value @ 550nm, see plot below:
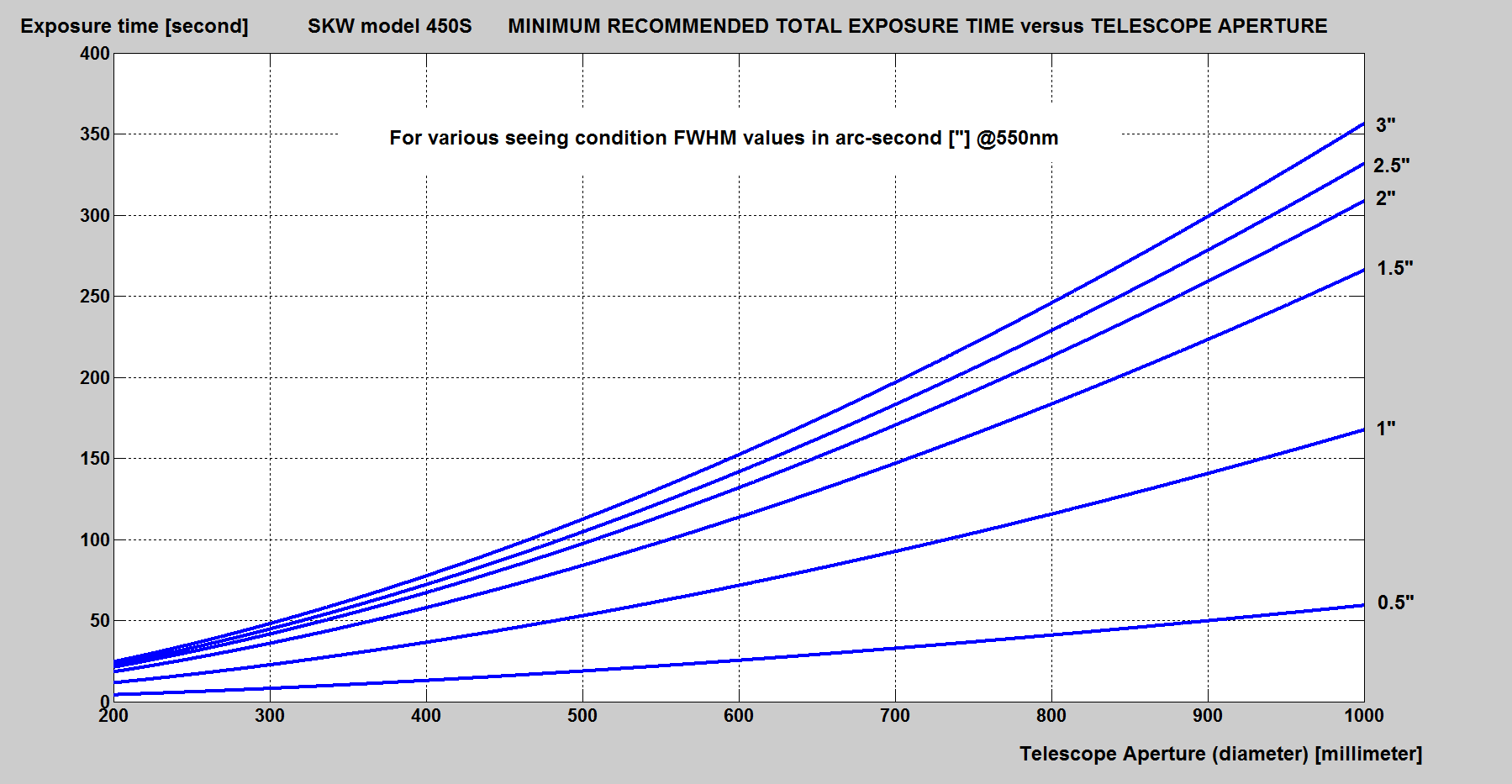
Recommended minimum total exposure time for best image analysis accuracy and acceptable inter image variability under the user selected local seeing at which the scope may operate, see plot below:
If the exposure is too large relative to the mount tracking performances (risk of elongated stars due to tracking drifts) one can takes several exposures for a cumulative total time identical to the value recommended in the plot. Those images can be either stacked, aligned (using image correlation) and averaged (without any other pre-processing or calibration). Alternatively they can all opened and analyzed in SKW (one at the time) while using the SKW collimator tool scatter plot for estimation of the average score cluster (blue dots), see SKW documentation for further information.
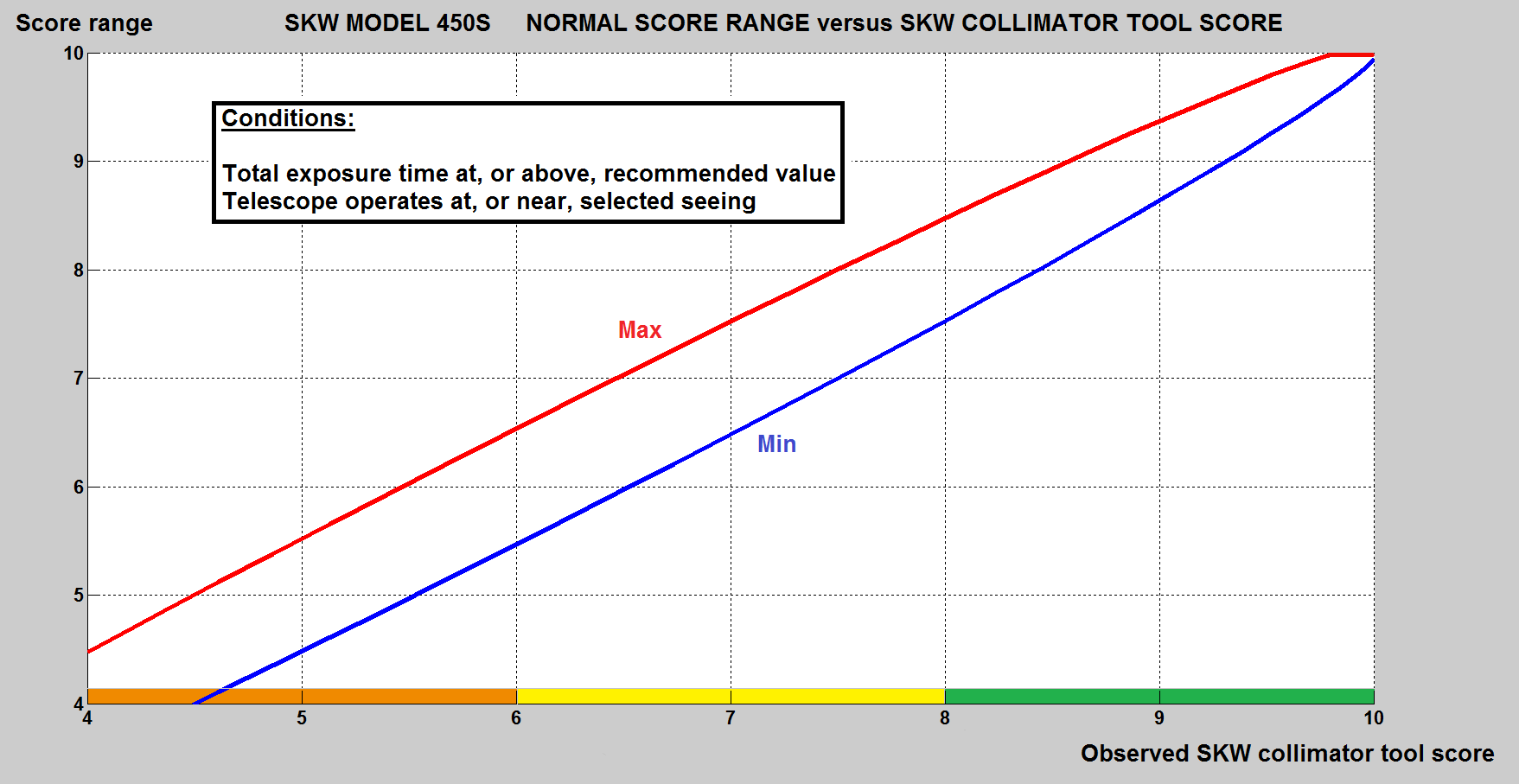
SKW collimator tool normal score range versus observed score, see plot below.
Assuming that the minimum recommended total exposure time, or longer, is used for the selected seeing FWHM value at which the scope operates.
When those conditions are met it is normal, and expected, for the observed SKW collimator tool scores to fluctuate within those ranges while the quality of the alignment remains essentially the same.The score fluctuation is the normal consequence of the seeing and inline with the analysis accuracy required for achieving a good alignment. As a consequence the final image quality and MTF are effectively seeing limited, any telescope left aberration are therefore negligible.
*
SKW manages licenses, models and credits locally on the user machine.
This means that there is no need to be connected to the Internet or any server when using the software.
It is handy when doing astronomy in remote isolated locations.
SKW uses block-chain technology to manage transaction history, in order to save memory space SKW/SKG limits, eventually, how many images it can
remember, after few thousands the oldest ones may trigger a new deduction of credits, again, when loaded and analyzed.
†
May not apply to some upgrades changing SKW capabilities. Those upgrades are usually for sale.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.